The connect and request timeout defaults have been updated from 20 to 60 seconds and a default value of 40 has been added for KERNEL_LAUNCH_TIMEOUT. The code ensures that KERNEL_LAUNCH_TIMEOUT is in the env and that the value of the request timeout is at least 2 greather than KERNEL_LAUNCH_TIMEOUT. This PR is port of the NB2KG PRs 35 and 38. |
||
|---|---|---|
| docs | ||
| docs-translations/ko-KR | ||
| git-hooks | ||
| notebook | ||
| tools | ||
| .babelrc | ||
| .bowerrc | ||
| .eslintignore | ||
| .eslintrc.json | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitmodules | ||
| .mailmap | ||
| .travis.yml | ||
| appveyor.yml | ||
| bower.json | ||
| codecov.yml | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.rst | ||
| COPYING.md | ||
| MANIFEST.in | ||
| package.json | ||
| README.md | ||
| readthedocs.yml | ||
| setup.cfg | ||
| setup.py | ||
| setupbase.py | ||
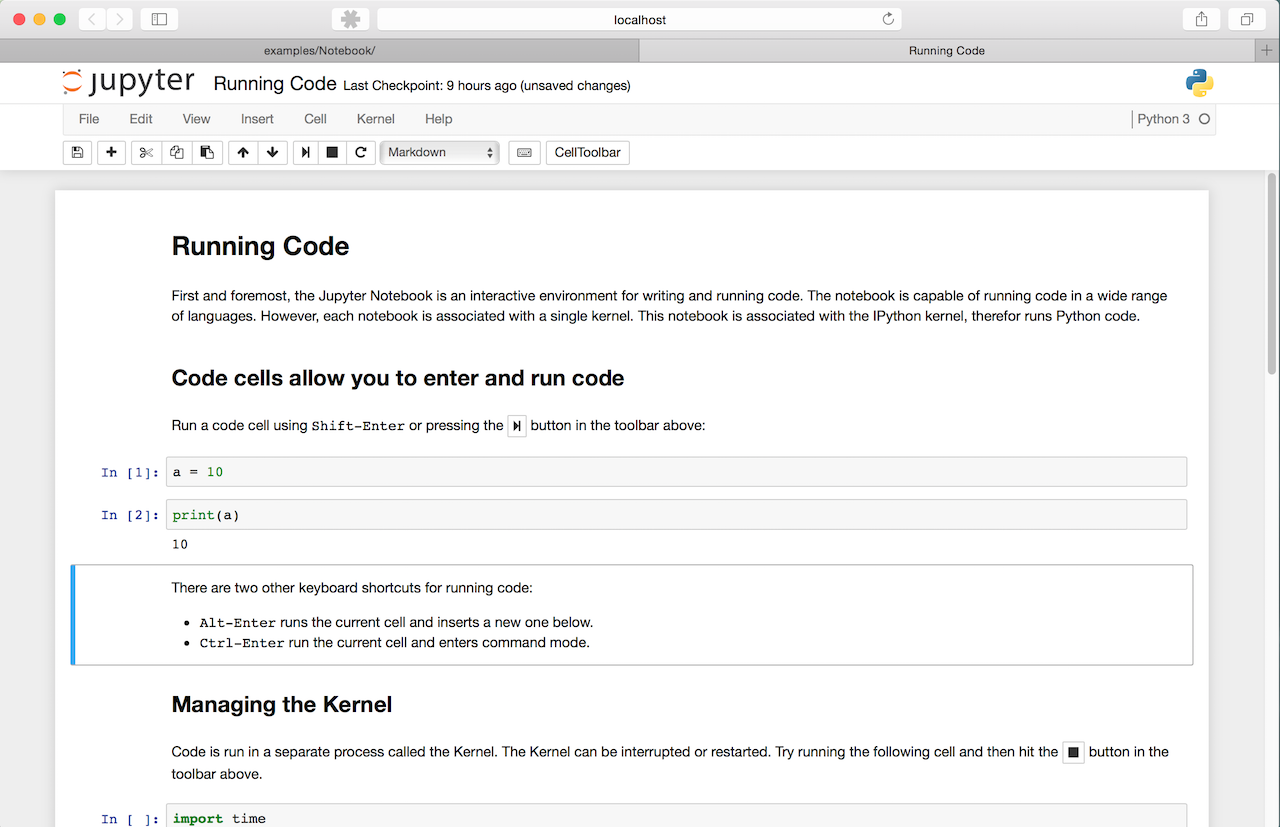
Jupyter Notebook
The Jupyter notebook is a web-based notebook environment for interactive computing.
Jupyter notebook, the language-agnostic evolution of IPython notebook
Jupyter notebook is a language-agnostic HTML notebook application for Project Jupyter. In 2015, Jupyter notebook was released as a part of The Big Split™ of the IPython codebase. IPython 3 was the last major monolithic release containing both language-agnostic code, such as the IPython notebook, and language specific code, such as the IPython kernel for Python. As computing spans across many languages, Project Jupyter will continue to develop the language-agnostic Jupyter notebook in this repo and with the help of the community develop language specific kernels which are found in their own discrete repos. [The Big Split™ announcement] [Jupyter Ascending blog post]
Installation
You can find the installation documentation for the Jupyter platform, on ReadTheDocs. The documentation for advanced usage of Jupyter notebook can be found here.
For a local installation, make sure you have pip installed and run:
$ pip install notebook
Usage - Running Jupyter notebook
Running in a local installation
Launch with:
$ jupyter notebook
Running in a remote installation
You need some configuration before starting Jupyter notebook remotely. See Running a notebook server.
Development Installation
See CONTRIBUTING.rst for how to set up a local development installation.
Contributing
If you are interested in contributing to the project, see CONTRIBUTING.rst.