| .circleci | ||
| .github | ||
| demo | ||
| gradio | ||
| gradio.egg-info | ||
| test | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| build-interface.py | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| MANIFEST.in | ||
| readme_template.md | ||
| README.md | ||
| render_readme.py | ||
| setup.py | ||
| upload_to_pypi.sh | ||
| workspace.code-workspace | ||
Welcome to Gradio
Quickly create customizable UI components around your models. Gradio makes it easy for you to "play around" with your model in your browser by dragging-and-dropping in your own images, pasting your own text, recording your own voice, etc. and seeing what the model outputs.
Gradio is useful for:
-
Creating demos of your machine learning code for clients / collaborators / users
-
Getting feedback on model performance from users
-
Debugging your model interactively during development
Getting Started
You can find an interactive version of this README at https://gradio.app/getting_started.
Quick Start
To get Gradio running with a simple example, follow these three steps:
1. Install Gradio from pip.
pip install gradio
2. Run the code below as a Python script or in a Python notebook (or in a colab notebook).
import gradio as gr
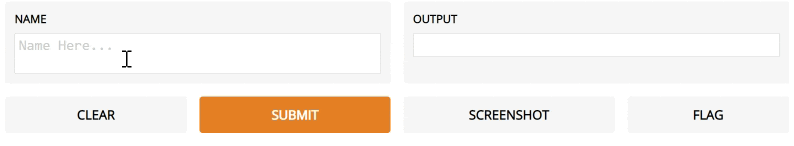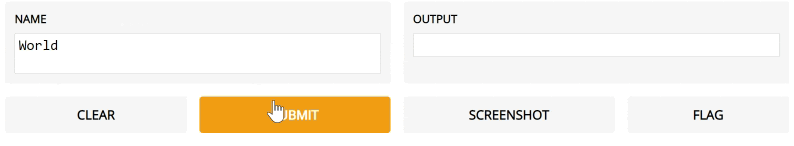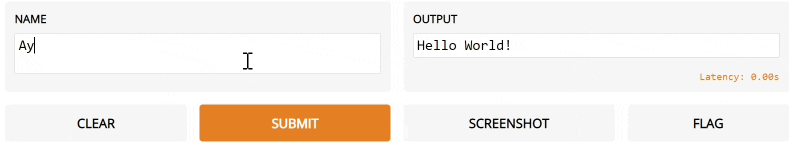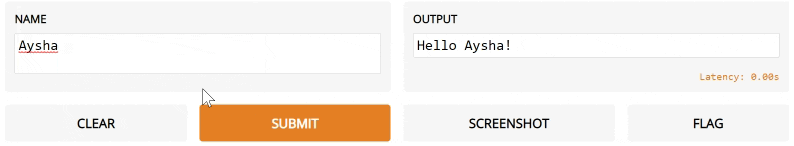
def greet(name):
return "Hello " + name + "!"
iface = gr.Interface(fn=greet, inputs="text", outputs="text")
iface.launch()
3. The interface below will appear automatically within the Python notebook, or pop in a browser on http://localhost:7860 if running from a script.
The Interface
Gradio can wrap almost any Python function with an easy to use interface. That function could be anything from a simple tax calculator to a pretrained model.
The core Interface class is initialized with three parameters:
fn: the function to wrapinputs: the input component type(s)outputs: the output component type(s)
With these three arguments, we can quickly create interfaces and launch() them. But what if you want to change how the UI components look or behave?
Customizable Components
What if we wanted to customize the input text field - for example, we wanted it to be larger and have a text hint? If we use the actual input class for Textbox instead of using the string shortcut, we have access to much more customizability. To see a list of all the components we support and how you can customize them, check out the Docs
import gradio as gr
def greet(name):
return "Hello " + name + "!"
iface = gr.Interface(
fn=greet,
inputs=gr.inputs.Textbox(lines=2, placeholder="Name Here..."),
outputs="text")
iface.launch()
Multiple Inputs and Outputs
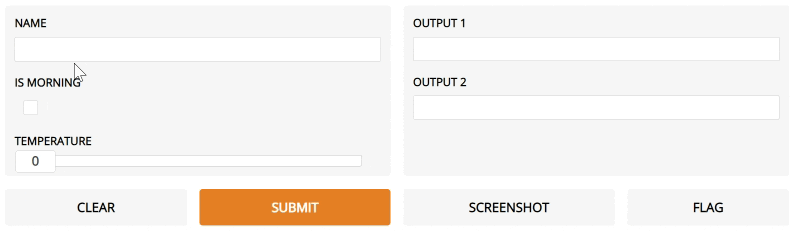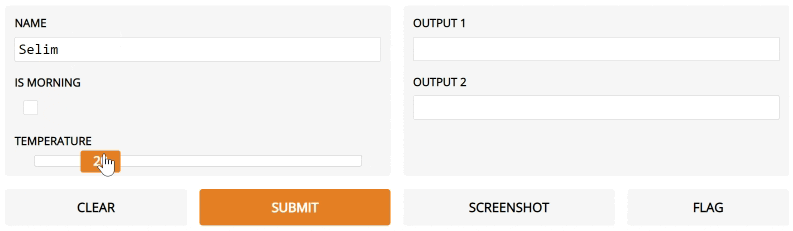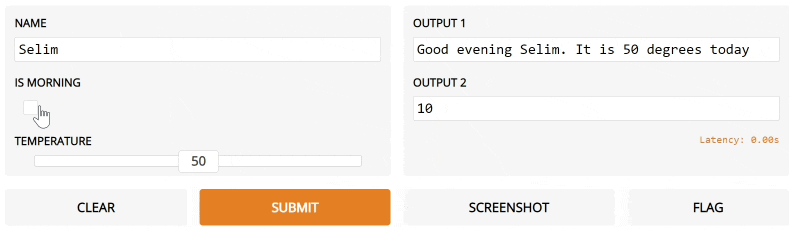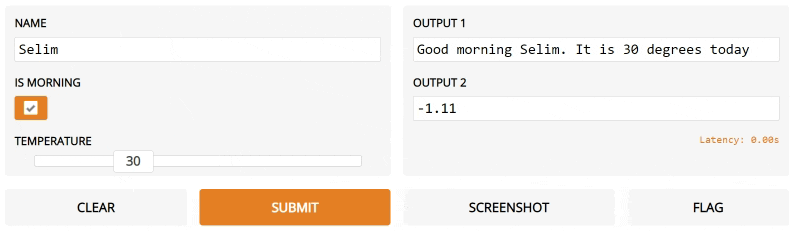
Let's say we had a much more complex function, with multiple inputs and outputs. In the example below, we have a function that takes a string, boolean, and number, and returns a string and number. Take a look how we pass a list of input and output components.
import gradio as gr
def greet(name, is_morning, temperature):
salutation = "Good morning" if is_morning else "Good evening"
greeting = "%s %s. It is %s degrees today" % (
salutation, name, temperature)
celsius = (temperature - 32) * 5 / 9
return greeting, round(celsius, 2)
iface = gr.Interface(
fn=greet,
inputs=["text", "checkbox", gr.inputs.Slider(0, 100)],
outputs=["text", "number"])
iface.launch()
We simply wrap the components in a list. Furthermore, if we wanted to compare multiple functions that have the same input and return types, we can even pass a list of functions for quick comparison.
Working with Images
Let's try an image to image function. When using the Image component, your function will receive a numpy array of your specified size, with the shape (width, height, 3), where the last dimension represents the RGB values. We'll return an image as well in the form of a numpy array.
import gradio as gr
import numpy as np
def sepia(img):
sepia_filter = np.array([[.393, .769, .189],
[.349, .686, .168],
[.272, .534, .131]])
sepia_img = img.dot(sepia_filter.T)
sepia_img /= sepia_img.max()
return sepia_img
iface = gr.Interface(sepia, gr.inputs.Image(shape=(200, 200)), "image")
iface.launch()
Additionally, our Image input interface comes with an 'edit' button which opens tools for cropping, flipping, rotating, drawing over, and applying filters to images. We've found that manipulating images in this way will often reveal hidden flaws in a model.
Example Data
You can provide example data that a user can easily load into the model. This can be helpful to demonstrate the types of inputs the model expects, as well as to provide a way to explore your dataset in conjunction with your model. To load example data, you provide a nested list to the examples= keyword argument of the Interface constructor. Each sublist within the outer list represents a data sample, and each element within the sublist represents an input for each input component. The format of example data for each component is specified in the Docs.
import gradio as gr
import random
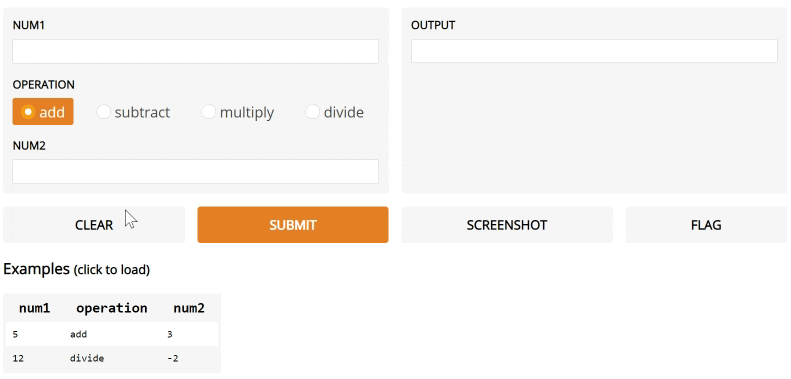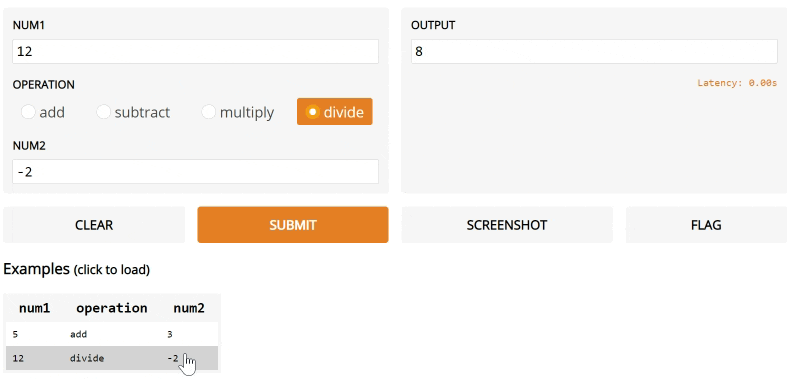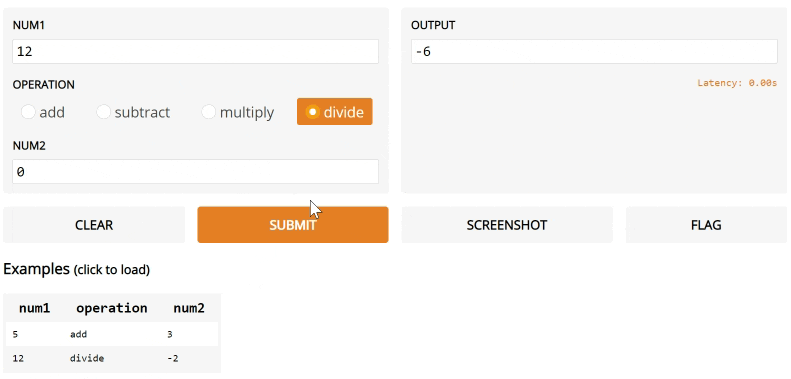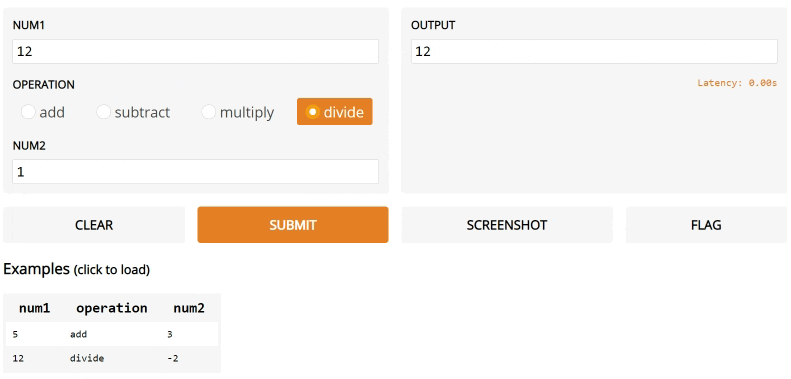
def calculator(num1, operation, num2):
if operation == "add":
return num1 + num2
elif operation == "subtract":
return num1 - num2
elif operation == "multiply":
return num1 * num2
elif operation == "divide":
return num1 / num2
iface = gr.Interface(calculator,
["number", gr.inputs.Radio(["add", "subtract", "multiply", "divide"]), "number"],
"number",
examples=[
[5, "add", 3],
[4, "divide", 2],
[-4, "multiply", 2.5],
[0, "subtract", 1.2],
],
)
iface.launch()
You can load a large dataset into the examples to browse and interact with the dataset through Gradio. The examples will be automatically paginated (you can configure this through the examples_per_page argument of Interface) and you can use CTRL + arrow keys to navigate through the examples quickly.
Flagging
Underneath the output interfaces, there is a button marked "Flag". When a user testing your model sees input with interesting output, such as erroneous or unexpected model behaviour, they can flag the input for the interface creator to review. Within the directory provided by the flagging_dir= argument to the Interface constructor, a CSV file will log the flagged inputs. If the interface involves file data, such as for Image and Audio components, folders will be created to store those flagged data as well.
For example, with the calculator interface shown above, we would have the flagged data stored in the flagged directory shown below:
+-- calculator.py
+-- flagged/
| +-- logs.csv
flagged/logs.csv
num1,operation,num2,Output
5,add,7,12
6,subtract,1.5,4.5
With the sepia interface shown above, we would have the flagged data stored in the flagged directory shown below:
+-- sepia.py
+-- flagged/
| +-- logs.csv
| +-- im/
| | +-- 0.png
| | +-- 1.png
| +-- Output/
| | +-- 0.png
| | +-- 1.png
flagged/logs.csv
im,Output
im/0.png,Output/0.png
im/1.png,Output/1.png
You can review these flagged inputs by manually exploring the flagging directory, or load them into the examples of the Gradio interface by pointing the examples= argument to the flagged directory. If you wish for the user to provide a reason for flagging, you can pass a list of strings to the flagging_options argument of Interface. Users will have to select one of the strings when flagging, which will be saved as an additional column to the CSV.
Sharing Interfaces Publicly & Privacy
Interfaces can be easily shared publicly by setting share=True in the launch() method. Like this:
gr.Interface(classify_image, "image", "label").launch(share=True)
This generates a public, shareable link that you can send to anybody! When you send this link, the user on the other side can try out the model in their browser. Because the processing happens on your device (as long as your device stays on!), you don't have to worry about any dependencies. If you're working out of colab notebook, a share link is always automatically created. It usually looks something like this: XXXXX.gradio.app. Although the link is served through a gradio link, we are only a proxy for your local server, and do not store any data sent through the interfaces.
Keep in mind, however, that these links are publicly accessible, meaning that anyone can use your model for prediction! Therefore, make sure not to expose any sensitive information through the functions you write, or allow any critical changes to occur on your device. If you set share=False (the default), only a local link is created, which can be shared by port-forwarding with specific users.
Share links expire after 6 hours.
Permanent Hosting
You can share your interface publicly and permanently by hosting on Gradio's infrastructure. You will need to create a Gradio premium account. First, log into Gradio on gradio.app and click Sign In at the top. Once you've logged in with your Github account, you can specify which repositories from your Github profile you'd like to have hosted by Gradio. You must also specify the file within the repository that runs the Gradio launch() command. Once you've taken these steps, Gradio will launch your interface and provide a public link you can share.
Advanced Features
Exploring Similar Examples with Embeddings
When you provide input to the function, you may wish to see if there are similar samples in the example dataset that could explain the behaviour of the function. For example, if an image model returns a peculiar output for a given input, you may load the training data into the examples dataset and see what training data samples are similar to the input you provided. If you enable this feature, you can click the Order by Similarity button to show the most similar samples from the example dataset.
Gradio supports exploring similar data samples through embeddings. Embeddings are a list of floats that numerically represent any input. To the embedding keyword argument of Interface, you must pass a function that takes the same inputs as the main fn argument, but instead returns an embedding that represents all the input values as a single list of floats. You can also pass the "default" string to embedding and Gradio will automatically generate embeddings for each sample in the examples dataset.
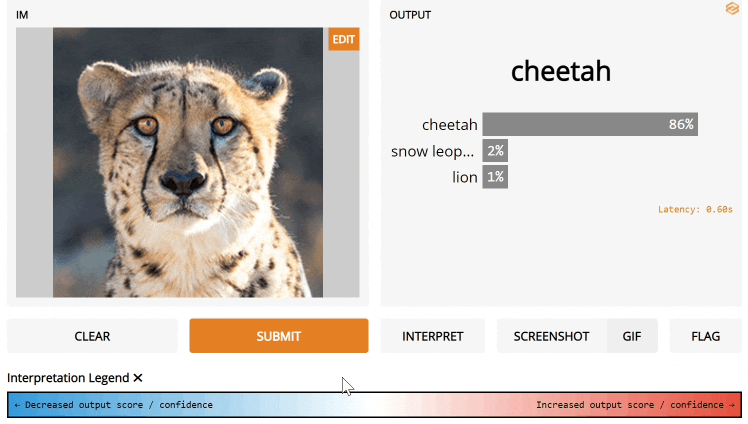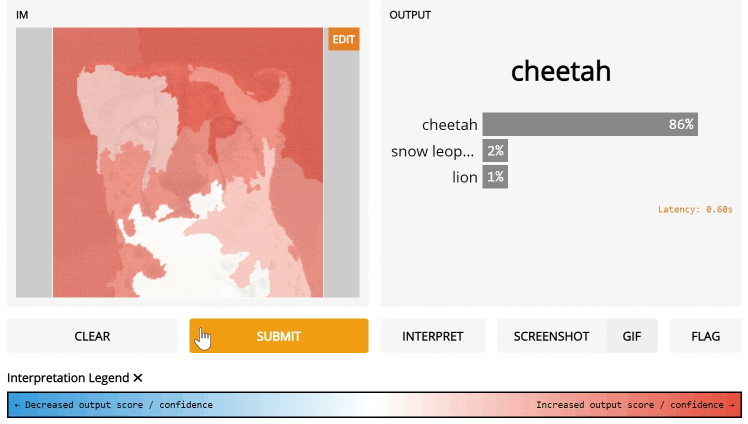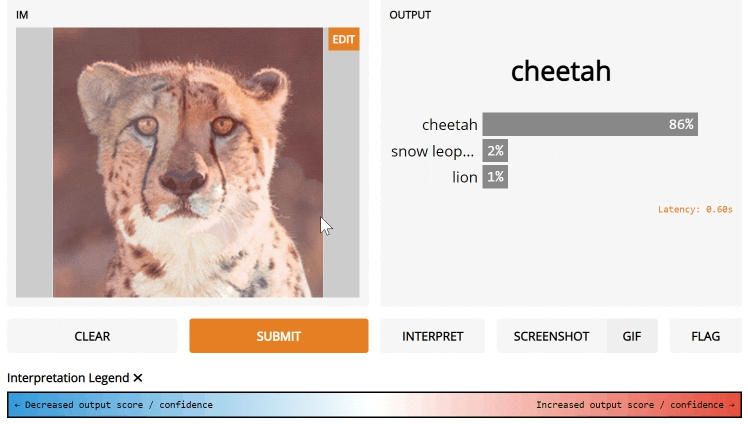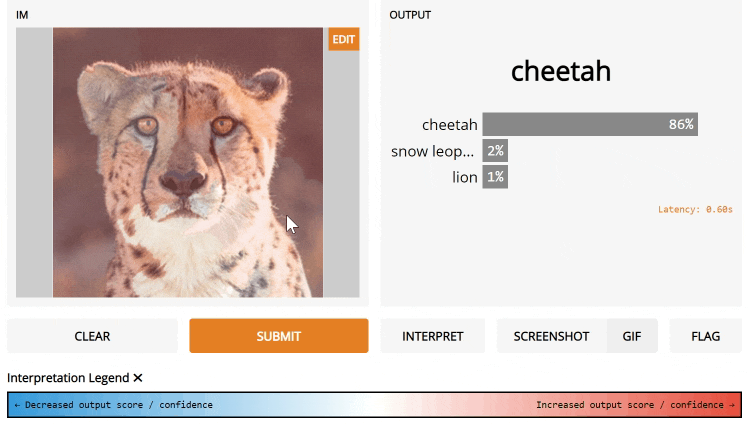
Interpretation
Most models are black boxes such that the internal logic of the function is hidden from the end user. To encourage transparency, we've added the ability for interpretation so that users can understand what parts of the input are responsible for the output. Take a look at the simple interface below:
import gradio as gr
import re
male_words, female_words = ["he", "his", "him"], ["she", "her"]
def gender_of_sentence(sentence):
male_count = len([word for word in sentence.split() if word.lower() in male_words])
female_count = len([word for word in sentence.split() if word.lower() in female_words])
total = max(male_count + female_count, 1)
return {"male": male_count / total, "female": female_count / total}
iface = gr.Interface(
fn=gender_of_sentence, inputs=gr.inputs.Textbox(default="She went to his house to get her keys."),
outputs="label", interpretation="default")
iface.launch()
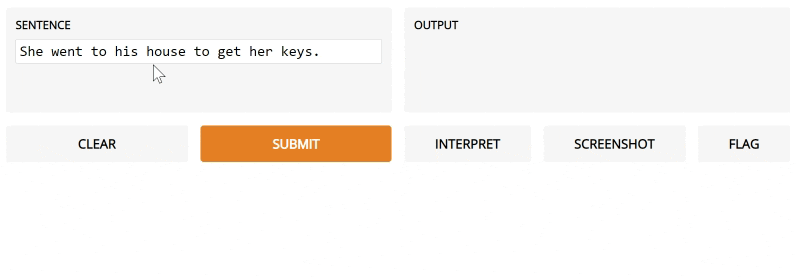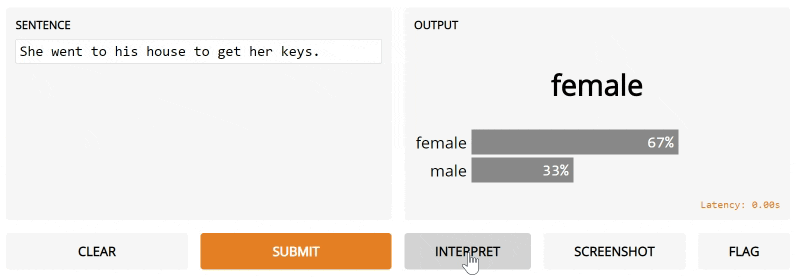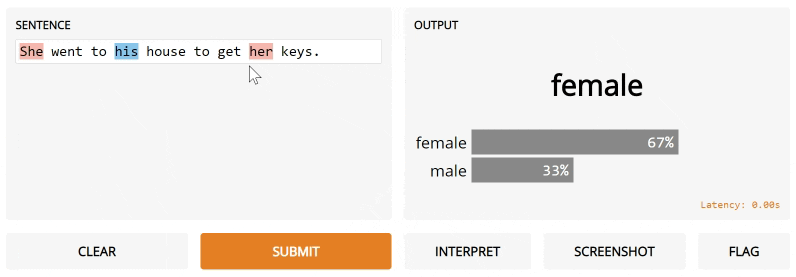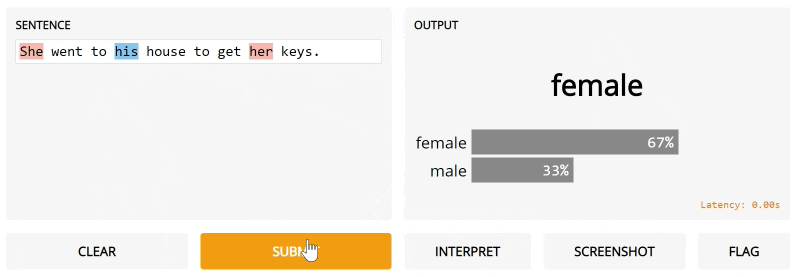
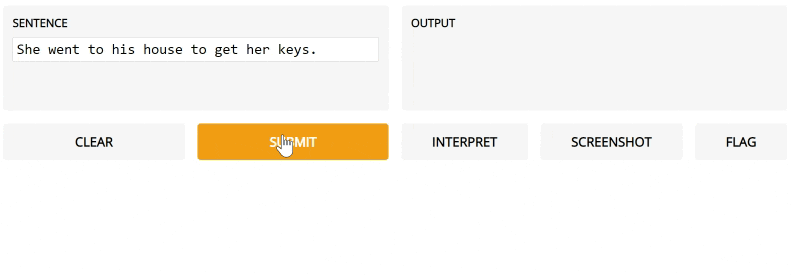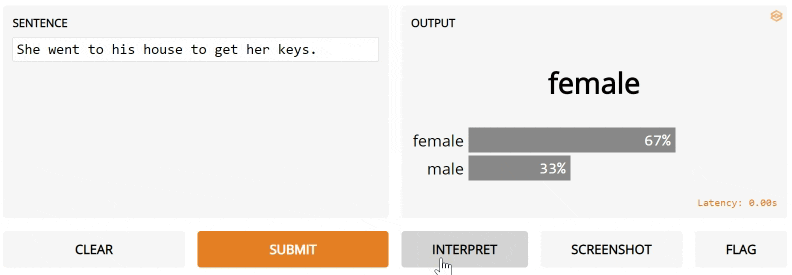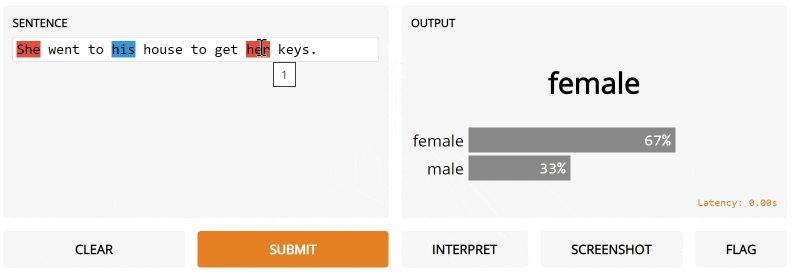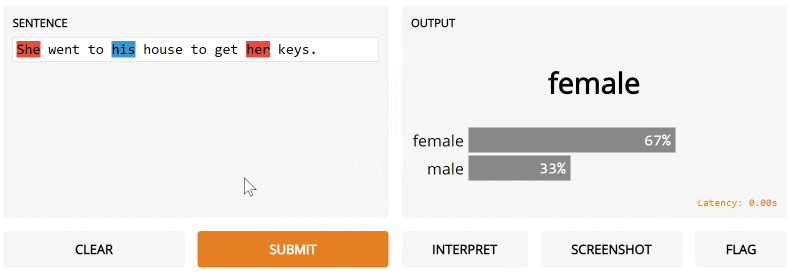
Notice the interpretation keyword argument. We're going to use Gradio's default interpreter here. After you submit and click Interpret, you'll see the interface automatically highlights the parts of the text that contributed to the final output orange! The parts that conflict with the output are highlight blue.
You can also write your own interpretation function. The demo below adds custom interpretation to the previous demo. This function will take the same inputs as the main wrapped function. The output of this interpretation function will be used to highlight the input of each input interface - therefore the number of outputs here corresponds to the number of input interfaces. To see the format for interpretation for each input interface, check the Docs.
import gradio as gr
import re
male_words, female_words = ["he", "his", "him"], ["she", "her"]
def gender_of_sentence(sentence):
male_count = len([word for word in sentence.split() if word.lower() in male_words])
female_count = len([word for word in sentence.split() if word.lower() in female_words])
total = max(male_count + female_count, 1)
return {"male": male_count / total, "female": female_count / total}
def interpret_gender(sentence):
result = gender_of_sentence(sentence)
is_male = result["male"] > result["female"]
interpretation = []
for word in re.split('( )', sentence):
score = 0
token = word.lower()
if (is_male and token in male_words) or (not is_male and token in female_words):
score = 1
elif (is_male and token in female_words) or (not is_male and token in male_words):
score = -1
interpretation.append((word, score))
return interpretation
iface = gr.Interface(
fn=gender_of_sentence, inputs=gr.inputs.Textbox(default="She went to his house to get her keys."),
outputs="label", interpretation=interpret_gender)
iface.launch()
If you use Gradio's default interpretation, the output component must be a label or a number. All input components are supported for default interpretation. Below is an example with image input.
import gradio as gr
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import json
from os.path import dirname, realpath, join
# Load human-readable labels for ImageNet.
current_dir = dirname(realpath(__file__))
with open(join(current_dir, "files/imagenet_labels.json")) as labels_file:
labels = json.load(labels_file)
mobile_net = tf.keras.applications.MobileNetV2()
def image_classifier(im):
arr = np.expand_dims(im, axis=0)
arr = tf.keras.applications.mobilenet.preprocess_input(arr)
prediction = mobile_net.predict(arr).flatten()
return {labels[i]: float(prediction[i]) for i in range(1000)}
iface = gr.Interface(
image_classifier,
gr.inputs.Image(shape=(224, 224)),
gr.outputs.Label(num_top_classes=3),
capture_session=True,
interpretation="default",
examples=[
["images/cheetah1.jpg"],
["images/lion.jpg"]
])
iface.launch()
Contributing:
If you would like to contribute and your contribution is small, you can directly open a pull request (PR). If you would like to contribute a larger feature, we recommend first creating an issue with a proposed design for discussion. Please see our contributing guidelines for more info.
License:
Gradio is licensed under the Apache License 2.0
See more:
You can find many more examples (like GPT-2, model comparison, multiple inputs, and numerical interfaces) as well as more info on usage on our website: www.gradio.app
See, also, the accompanying paper: "Gradio: Hassle-Free Sharing and Testing of ML Models in the Wild", ICML HILL 2019, and please use the citation below.
@article{abid2019gradio,
title={Gradio: Hassle-Free Sharing and Testing of ML Models in the Wild},
author={Abid, Abubakar and Abdalla, Ali and Abid, Ali and Khan, Dawood and Alfozan, Abdulrahman and Zou, James},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.02569},
year={2019}
}